 Overview
Overview
What is the impact of generative AI tools on engineering education at minority-serving institutes (MSIs)?
Specifically, introductory computer programming (CS1) classes are most impacted with the advent of AI tools that can write computer programs easily. Since it is often a required course, a large base of students is impacted by generative AI due to its capacity to solve most in-class activities, assignments, and projects traditionally used in such courses.
Our goal in this research is to devise strategies to optimize the teaching and learning with AI tools in computing classrooms and engineering education in general for advancement of student learning.
Specific themes in this project area include:
- Can we model self-efficacy of students in engineering classrooms by quantifying student reflections?
- How does the prevalence of AI impact performance equity and creativity in engineering education classrooms? Do hands-on projects impact student creativity?
- Build and deploy open-source tools for AI-based assessment, effective hands-on learning, and AI-powered quantification of mixed educational data.
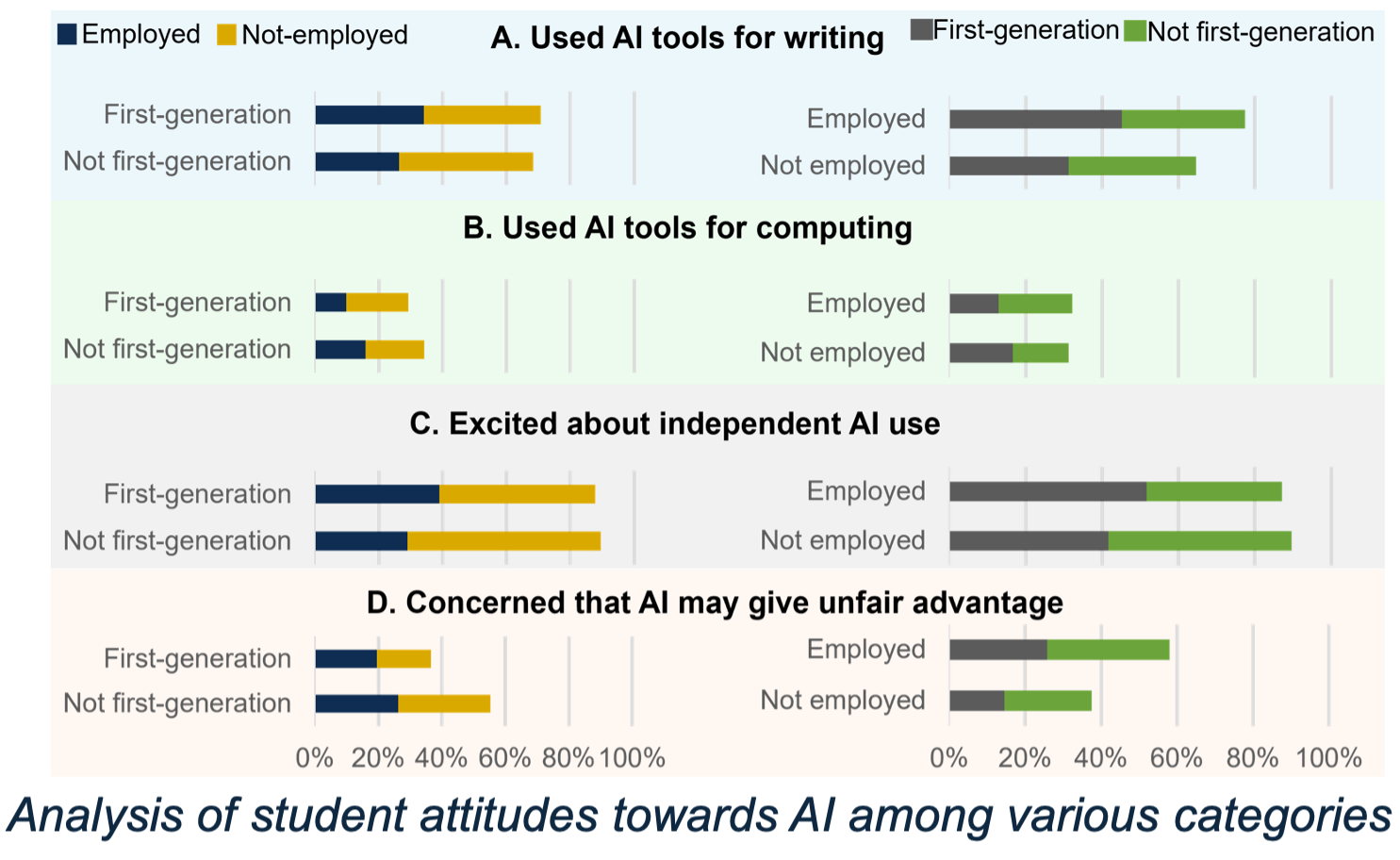
Preliminary surveys indicate that students are actively using AI for writing and computation, and at the same time are also excited to learn effective ways to use AI to improve their learning. A categorical analysis reveals trends on how students AI use varies depending on their prior preparedness, privileges of technological support structures, and the time that students have on their hands to experiment with AI.
Specific research areas that we are exploring include:
- GPT-based codebooks for quantification of self-efficacy
- Design of hands-on open-ended engineering education projects
- Analysis of qualitative and quantitative data on effective use of AI among students
- AI-based assessment tools
This research is led by Dr. Ayush Pandey.

